|
Hydrazine (anhydrous) is a clear, fuming, corrosive liquid with an ammonia-like
odor; melting at 1.4 C, boiling at 113.5 C, specific gravity 1.011. It is very
soluble in water and soluble in alcohol. It decomposes on heating or exposure to
UV to form ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen, which may be explosive with a blue
flame when catalysed by metal oxides and some metals such as platinum or Raney
nickel. It is prepared from ammonia with chloramine in the presence of glue or
gelatin (to inhibit decomposition of the hydrazine by unreacted oxidants) as the
hydrate form usually (100% monohydrate contains 64% by weight hydrazine).
Hydrazine is also prepared from sodium hypochlorite with urea in the presence of
glue or gelatin. Botht ammonia and amines are nitrogen nucleophiles which
donate electrons (they are Lewis bases). But hydrazine (diamine) has much
stronger nucleophilicity which makes it more reactive than ammonia. Hydrazine
has dibasic and very reactive properties. Hydrazine is used as a component in
jet fuels because it produce a large amount of heat when burned. Hydrazine is
used as rocket fuel. Hydrazine is used as an oxygen scavenger for water boiler
feed and heating systems to prevent corrosion damage. Hydrazine is used as a
reducing agent for the recovery of precious metals. It is used as a
polymerization catalyst and a chain extender in urethane coatings. It and its
derivatives are versatile intermediates. They have active applications in
organic synthesis for agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, photographic, heat
stabilizers, polymerization catalysts, flame-retardants, blowing agents for
plastics, explosives, and dyes. Recently, hydrazine is applied to LCD (liquid
crystal displays) as the fuel to make faster thin-film transistors. Hydrazone is a
compound containing the group -NH·N:C-. It is formed from a condensation
reaction aldehydes or ketones with hydrazines (commonly phenylhydrazine). It is
used as a an exotic fuel. Aromatic hydrazones are used to form indoles by a ring
closure reaction (Fischer synthesis). Hydrazones and hydrazines are converted to
aldehydes and ketones to corresponding hydrocarbons by heating the carbonyl
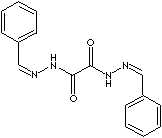
compound with sodium ethoxide (Wolf-Kishner reduction). Oxalic acid bis(benzylidenehydrazide)
is used as a plastic stabilizer
especially
for polyolefins contacting copper and copper containing
alloys. |